SoC design : millimeter-wave receivers
We develop innovative solutions based on the specific features offered by CMOS technologies to optimize mixer performance. These include the implementation of discrete-time analog systems, using sampling techniques or parallelizing series of N-path cells.
Over the past two decades, the remarkable increase in the frequency of CMOS transistors, achieved by progressively reducing dimensions, has opened up numerous possibilities in the fields of imaging, detection, and wireless communications. Unfortunately, this performance enhancement is accompanied by a reduction in the power handling capability of transistors, thereby limiting the performance of systems designed in this manner. Integating a CMOS receiver front-end poses many challenges at millimeter-wave frequencies, particularly at the mixer level, which emerges as one of the main contributors to noise and non-linearity in the chain.
For several years, we have been developing innovative solutions leveraging the specificities offered by CMOS technologies to optimize mixer performance. Among these, the implementation of discrete-time analog systems is becoming widespread, using sampling techniques or parallelizing series of N-path cells.
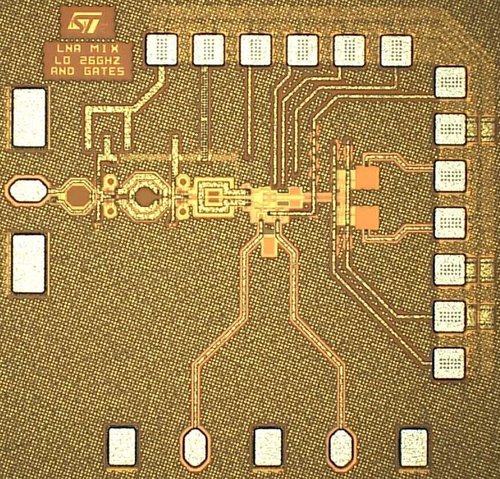
The photo on the right illustrates the most recent work carried out in collaboration with STMicroelectronics, aiming to integrate a sampled mixer at 77 GHz within a receiver chain for embedded automotive radar, achieving state-of-the-art results.