Integrating diagnosis and prediction for predictive maintenance Diagnostic/prognostic integration for predictive maintenance
Prognosis is increasingly used in industrial applications, particularly for predictive maintenance. Diagnosis and prognosis are highly correlated: diagnosis determines the set of faulty components explaining the observed malfunctions, while prognosis determines the future state of the components.
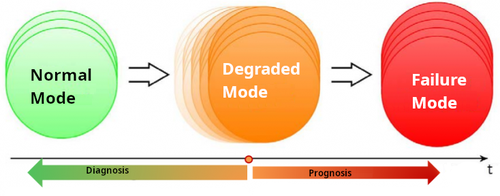
Prognosis is increasingly used in industrial applications, particularly for predictive maintenance. Diagnosis and prognosis are highly correlated: diagnosis determines the set of faulty components explaining the observed malfunctions, while prognosis determines the future state of the components based on aging/degradation models of the monitored system. These techniques can be used to determine the state of health and assess the residual lifetime of system components. They can use physics-based models, statistical data analysis, learning and/or estimation methods. DISCO studies the coupling of system diagnostics and prognostics with a view to refining possible strategies integrating corrective and predictive maintenance.
FOCUS
Diagnostic/prognostic prerequisite model
The team has developed a generic model of equipment aging that establishes a set of prerequisites for setting up a prognostic process on a complex, heterogeneous system, in conjunction with a process for diagnosing degradation and stress factors. This type of model has been applied to a stator in permanent magnet synchronous machines (landing gear) (Safran CIFRE collaboration).
Interval analysis and computation for diagnosis/prognosis
DISCO has developed a method based on the theory of interval calculus to solve the problem of equipment health management, which has been applied to the health management of a control valve (A320 Neo) for which a demonstrator has been implemented (Prognospice).
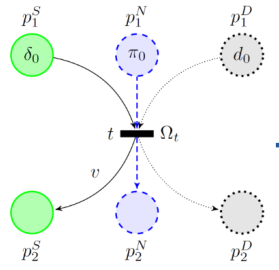
Formalism for particulate hybrid Petri nets
DISCO is developing a formalism which aims to model the dynamics of a hybrid system, both from a functional and behavioral point of view, and from the point of view of degradation and future aging. This unique formalism can be used as the basis for a diagnostic function (fault diagnosis, failure diagnosis) consistent with a prognostic function.