Jido
Localisation
Several modules are involved in the localization of the robot.
First the jloco module, which interfaces low level software provided by the manufacturer and which exports in a poster the position computed by the odometry and corrected by the gyroscope.
This position gives a good estimate of the motions of the robot. It is associated with a covariance matrix deduced from a probabilistic model error.
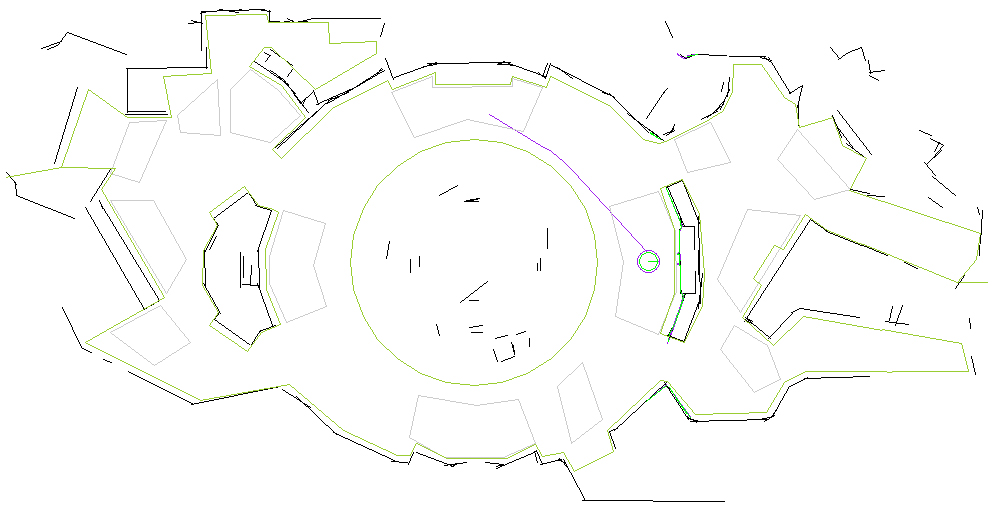
To localize itself within its environment the robot uses a SICK laser, controlled by the sick module, that exports at the required rate the laser echoes together with segments deduced from aligned echoes. Another module, segloc, matches these segments with segments previously recorded in a map thanks to a classical SLAM procedure. However the map is effectively updated only during exhibition closing time (no public).
The various uncertain positions exported by the modules rflex and segloc are merged by pom, the position manager module. This module is able to integrate positions computed at various frequencies and even to propagate "old" position data. Various fusion strategies can be selected like Kalman fusion or integration of the measured motions relatively to the most reliable positions. The supervisor is informed in case of localization problems with one of the modules, fusion difficulties or significant uncertainties on the position. Depending on the problem and the context, various strategies are applied. It is important to note that the pom module allows to centralize the robot positions and to export one and only one reference position. All the other system components do not need to know how this position is obtained. This procedure can change dynamically without disturbing the position consumers. It is a very important mechanism to manage redundancy and an essential feature for this critical function.
On top of this geometric positioning, several topological zones corresponding to places of special interest ("TARGETS"), to dangers for the navigation ("OBSTACLES") not always visible by the robot sensors like prominent or transpar- ent furniture), or to other special areas ("SPECIAL") have been defined in the environment. The zone module continuously monitors entrance and exit of the robot from these zones and informs the supervisor.